1.1 INTRODUCTION:
Chemistry is defined as that branch of science which deals with the composition and properties of matter and the changes that matter undergone by various interactions. A chemical compound is formed as a result of a chemical change and in this process different type of energies such as heat, electrical energy, radiation etc. are either absorbed or evolved. The total mass of the substance remains the same throughout the chemical change.
1.2 CHEMICAL ACTION OR REACTION:
When a chemical change occurs, a chemical action is said to have taken place. A chemical change or chemical action is represented by a chemical equation. The matter undergoing change in known as reactant and new chemical component formed is known as product.
1.2 (a) Characteristics of a Chemical Reaction:
When we heat sugar crystals they melt and on further heating they give steamy vapour, leaving behind brownish black mass. On cooling no sugar crystals appears. Thus change which takes place on heating sugar is a chemical change and the process which brings about this chemical change is called chemical reaction.
- In this reaction the substance which take part in bringing about chemical change are called reactants.
- The substance which are produced as a result of chemical change are called products.
- These reactions involve braking and making of chemical bonds.
- Product(s) of the reaction is/are new substances with new name(s) and chemical formula.
- It is often difficult or impossible to reverse a chemical reaction.
- Properties of products formed during a chemical reaction are different from thos of the reactants.
- Apart from heat other forms of energies are light and electricity which are also used in carrying out chemical changes.
In all chemical reactions, the transformation from reactants to products is accompanied by various characteristics, which are-
(i) Evolution of gas : Some chemical reactions are characterized by evolution of a gas.
- When zinc metal is treated with dilute sulphuric acid, hydrogen gas is evolved. The hydrogen gas burns with a pop sound.
Zn (s) + H2SO4 (dilute) 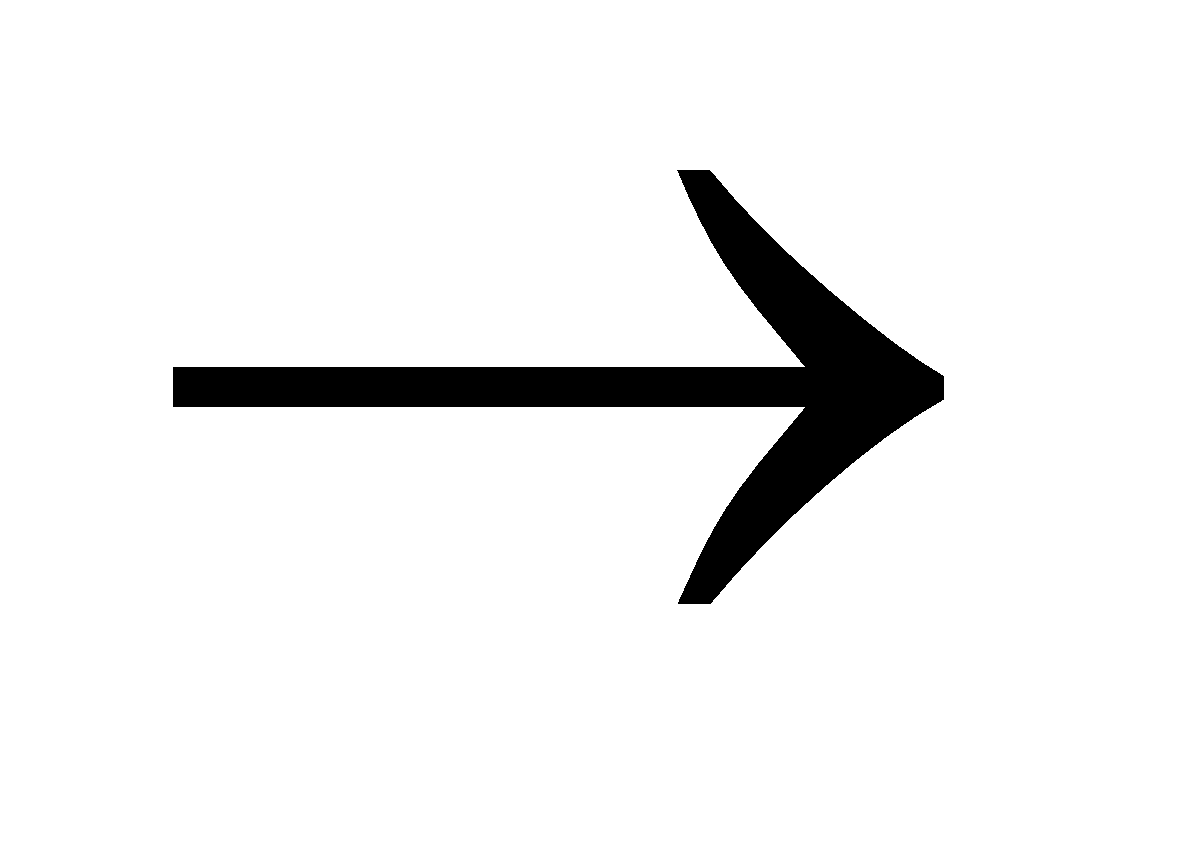 ZnSO4 (aq) + H2(g)
ZnSO4 (aq) + H2(g)
- When washing soda is treated with hydrochloric acid, it gives off colorless gas with lots of effervescence.
Na2CO3(s) + 2HCI  2NaCI (aq) + H2O(I) + CO2(g)
2NaCI (aq) + H2O(I) + CO2(g)
- 2NaNCO3 (s)
Na2SO3 (s) + H2O
+ CO2 (g)
Sodium hydrogen Sodium carbonate Water Carbon dioxide
carbonate